Property tax is a very important tax in terms of collection. However, sometimes one may have one or more properties but not such a good income and thus, property tax may turn out to be too difficult. Fortunately there are several forms of property tax relief that can provide a lot of ease during low income periods. These types of relief fall into different categories and with the help of an experienced irs tax attorney, tax reductions can be achieved in different ways.
What is the purpose of property taxes?
Property taxes are a main source of funding for local government units, which includes libraries, townships towns & cities, counties, and other special districts including solid waste districts and fire districts. Property taxes are collected and administered by local government officials. These funds are used to pay for a variety of services including welfare; police and fire; new construction and maintenance of buildings; local infrastructure like roads & streets, highways; and the operations, including salaries, of the local units of government.
Property taxes are an ad valorem tax, which means that they’re proportionately allocated to each taxpayer in accordance with the taxpayer’s property value. The state-wide average revenue distribution for each property tax dollar’s as follows:
- County: $0.17
- Township: $0.03
- City/Town: $0.19
- School: $0.41
- Library: $0.04
- Special Unit: $0.07
- Redevelopment: $0.08
What types of property tax relief are available to taxpayers?
- Exemptions – an exemption’s a partial or full waiver of property tax liability for a certain property. Generally, exemptions only are available in limited circumstances, like for not-for-profit organizations, religious groups, and economic development purposes.
- Deductions – a deduction’s a subtraction of evaluated value for a property before the tax liability calculation. Deductions are the most common types of property tax relief that are available for taxpayers and include relief for disabled citizens, veterans, mortgaged property, and primary residences (homesteads), to name a few.
- Credits – a credit’s a type of property tax relief that’s directly applied to the tax liability after it’s calculated initially. Common property tax credits are inclusive of the local property tax replacement credit and the circuit breaker credit.
The different categories of property tax relief address different problems. These categories include Property tax relief for senior citizens, property tax relief for first-time home buyer income tax, and property tax relief for low-income taxpayers, property tax relief for individual income taxpayers, as well as property tax relief for long-term owners. Also, there is an exemption for property tax for homestead.
Property Tax Relief for Senior Citizens
Property tax relief for senior citizens makes sense because it protects those who due to retirement have a lower income and thus cannot afford to pay the same taxes as before retiring. The income reduction experienced by most senior citizens and the higher costs of health insurance and other expenses justifies this type of relief that provides their budget with some ease.
Property Tax Relief for First Time Home buyers
Those purchasing a property for the first time usually do so to establish themselves and often start a family. The government in order to provide protection to this particular situation offers reductions and exceptions on first time homebuyer’s property tax and rebates or refunds that can be applied to income tax. It also contributes to encouraging construction and house loan businesses.
Property Tax Relief for Low Income Tax Payers
There are also people that have low income even if not retired. For those with a low income there are also tax relief solutions. Just like with senior citizens, people with low income cannot afford high taxes since they need their income to cope with other expenses. Recognizing this fact, the government provides reductions on property tax for those who can show proof of a low income that would not otherwise let them afford the full tax returns.
Property Tax Relief for Individual Income Tax Payers
Individual Income tax Credit provides those with low income a refund of taxes that includes property tax. This tax credit is one of the most important poverty reduction tools of the country (other countries use it too) as it returns important amounts paid on taxes to those who have low earnings. There is a high amount of uncollected tax credits from people that either do not know or will not take the trouble to fill out the forms needed to collect this money. We always suggest those with low income to resort to nonprofit organizations that can aid in the process of obtaining Individual Earned Income Tax Credit.
Property Tax Relief for Longer Term Owners
Long-term owners can obtain reductions on the amount of money they pay for property tax. Regulations defer from one state to another but most of them have some sort of differential taxation between new owners and long-term owners. For further information on this issue and all of the above, you should consult with a consultant agency specializing in taxes. There are also nonprofit organizations that can provide you with assistance and information on these subjects.
How is the value of my property determined?
The billing cycle and tax assessment starts with the assessor’s valuation of your property. Just like other states, properties in Indiana are valued with the use of mass appraisal techniques. With mass appraisal, your property’s looked at in conjunction with other properties in your area. Assessors consider condition, grade, and age. Lastly, in a process called “trending” or annual adjustment, each year real property sales data is used to determine if the value of properties in your area should change to match the market value found in the sales of recent properties.
(Before 2002, the property was re-evaluated every five to ten years. That left taxpayers with a huge change in their evaluations between reassessments, which often lead to sudden upsurges in property tax bills.)
Learn more about Annual Adjustment and Reassessment.
How is property tax calculated?
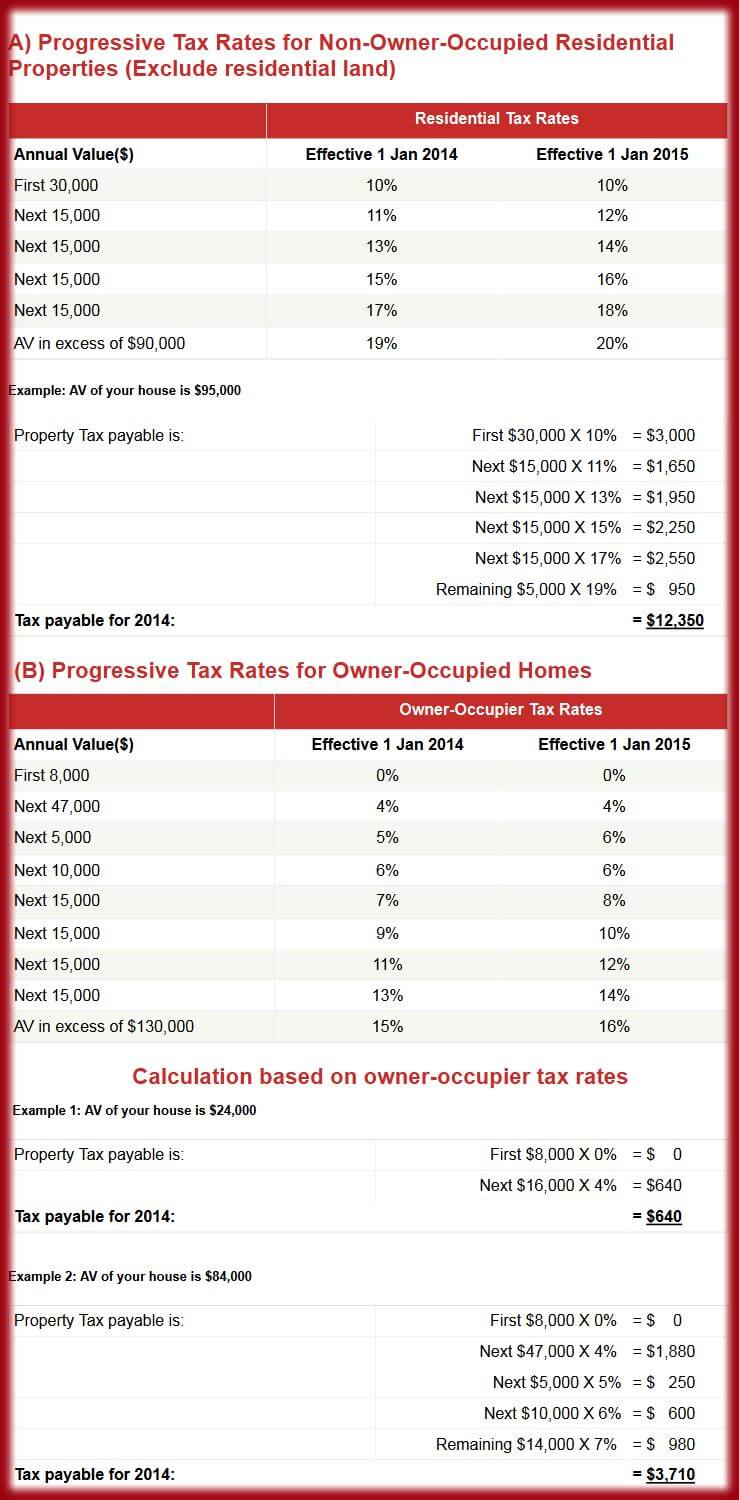
The Government has announced the introduction of progressive tax rates for all residential properties from 1 Jan 2014 and 1 Jan 2015. Other properties (like residential land, industrial and commercial buildings), will continue to be taxed at the Non-Residential Tax rate of 10%.
Related Posts:
– When And Why Would You Need An IRS Tax Attorney – The Inside Scoop
– Top 10 Tips for Filing IRS Tax Returns in 2014
– What is a Back Tax? and How to Negotiate Back Taxes With IRS?